How China’s Metal Export Ban Will Impact the U.S.

Date
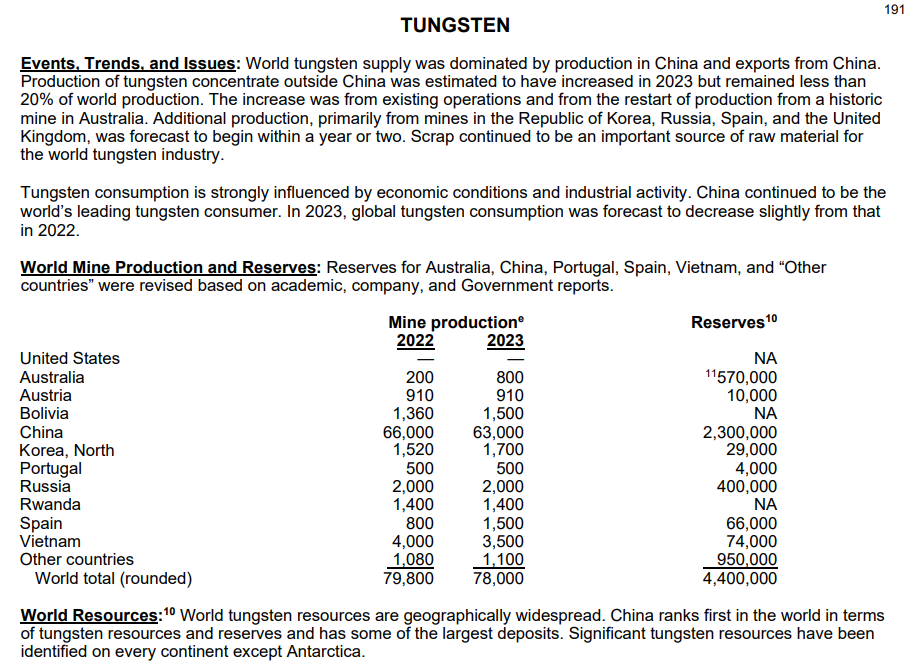
World Tungsten Production and ReservesSource: www.USGS.com
How China’s Metal Export Ban Will Impact the U.S. Scrap Metal Recycling Industry
China’s recent export ban on critical materials such as tungsten and other “superhard metals” has created significant challenges for industries worldwide. These materials, primarily found in the D-block of the periodic table, are important for advanced manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. For the U.S. scrap metal recycling industry, this geopolitical shift presents opportunities to alleviate supply chain constraints and establish a more sustainable metals economy.
The Importance of Superhard Metals
Superhard metals like tungsten are known for their exceptional hardness, high melting points, and resistance to wear and corrosion, making them vital for cutting tools, abrasives, and high-performance alloys. Tungsten carbide, for example, is a cornerstone material in industrial machinery and defense applications. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, China produced approximately 85% of the world’s tungsten in 2022, underscoring the critical reliance on Chinese exports (USGS, 2023). Other metals impacted by potential upcoming restrictions from China include molybdenum and cobalt, which are also essential for creating heat-resistant alloys and industrial tools.
The Impact on U.S. Supply Chains
China’s decision to restrict exports is widely regarded as a response to growing trade tensions with the U.S. and Western restrictions on China’s access to advanced semiconductor technology. The ban will force manufacturers in the U.S. to seek alternative sources for these essential materials, turning the spotlight on domestic scrap metal recycling. This shift could fundamentally reshape how the U.S. sources and processes tungsten and other d-block metals. According to the Associated Press, the ban highlights the urgency of reducing dependency on foreign suppliers by bolstering domestic recycling and mining efforts.
Opportunities for the U.S. Scrap Recycling Industry
The export ban is likely to result in a surge in demand for recycled metals. As manufacturers scramble to secure alternative supplies, the recycling industry will need to scale up operations to meet this demand. Recyclers are expected to see increased interest in high-value scrap materials such as tungsten alloys, used cutting tools, and worn-out industrial machinery. This shift may drive innovation in the recovery processes for these superhard materials, with advancements in technologies like chemical leaching and electrolysis enabling higher yields from recycled sources. Additionally, the heightened demand may lead to better pricing for scrap metal, benefiting recyclers and encouraging more collection of recyclable materials.
Challenges Facing the Industry
While the opportunities are significant, the scrap metal recycling industry faces challenges in scaling up to meet this demand. Processing superhard metals requires specialized equipment and expertise, and the capital investment needed to expand facilities and adopt new technologies could be substantial. Moreover, compliance with environmental regulations will remain a critical factor in expanding operations sustainably. Raising awareness among businesses and consumers about the value of recycling superhard metals will also be essential for increasing the collection of scrap.
Building a Resilient Supply Chain
The U.S. government may play a critical role in mitigating the effects of China’s export ban. Policies aimed at incentivizing recycling, such as grants for advanced recovery technologies and tax breaks for recyclers, could help strengthen the domestic supply of critical metals. Collaboration between manufacturers and recyclers will also be vital to develop closed-loop systems that maximize the recovery and reuse of valuable materials. By taking these steps, the U.S. can build a more resilient and self-reliant supply chain for superhard metals.
China’s export ban on superhard metals emphasizes the vulnerability of global supply chains and the importance of recycling in addressing critical material shortages. For the domestic scrap metal industry, this challenge offers an opportunity to lead the way in sustainable sourcing and recovery of essential materials. By investing in advanced technologies, strengthening partnerships, and scaling operations, recyclers can not only meet the growing demand but also secure their place as key players in the global metals economy.


