Meeting U.S. Critical Mineral Demands

Date
to U.S. Security Source: www.elements.visualcapitalist.com
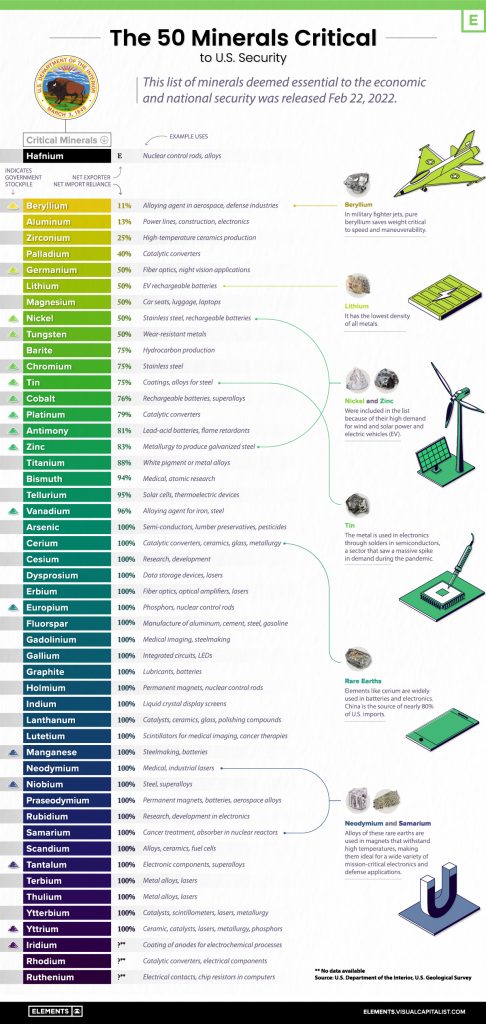
The D-Block of the periodic table holds a treasure trove of essential metals crucial for technological advancements, defense applications, and overall national security. Recognizing the strategic importance of these elements, the U.S. Department of the Interior has identified a list of “50 critical minerals“. Meeting the escalating demand for these minerals requires innovative solutions, and recycling metals from the D-Block presents a promising strategy to enhance the United States’ resource security.
The Significance of D-Block Metals
The D-Block, or transition metals, contains elements such as Vanadium, Chromium, Manganese, Cobalt, Nickel, Zinc, Yttrium, Zirconium, Niobium, Ruthenium, Rhodium, Palladium, Hafnium, Tantalum, and Tungsten. These metals play pivotal roles in various industries, including electronics, aerospace, and defense, making them indispensable for the nation’s technological progress and security.
Challenges in the Critical Mineral Supply Chain
The demand for critical minerals has surged with the rapid evolution of technology and the increasing complexity of defense systems. However, the supply chain for these minerals faces challenges such as geopolitical uncertainties, supply chain vulnerabilities, and environmental concerns associated with traditional mining practices.
Recycling D-Block Metals as a Strategic Solution
Recycling metals from the D-Block presents a strategic and sustainable solution to address the rising demand for critical minerals. The following aspects highlight the benefits of recycling these metals:
Circular Economy Approach
Recycling D-Block metals aligns with the principles of a circular economy, where resources are reused and repurposed. Recovering these metals from end-of-life products, electronic waste, and industrial processes reduces the need for new mining activities, promoting a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach.
Resource Conservation
By recycling D-Block metals, the U.S. can conserve its finite mineral resources. Rather than relying solely on primary mining operations, recycling extends the lifespan of existing resources, ensuring a more responsible and efficient use of critical minerals.
Reduced Dependency on Foreign Sources
Establishing robust recycling systems for D-Block metals can reduce the nation’s dependency on foreign sources. This is particularly important for enhancing national security, as it mitigates the risks associated with geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and fluctuations in global mineral markets.
Government Support and Industry Collaboration
To fully harness the potential of recycling D-Block metals, government support and collaboration within the industry are essential. Incentives, policies, and regulations that promote sustainable practices and resource conservation can encourage businesses to adopt recycling technologies and establish efficient collection and processing systems.
As the demand for critical minerals continues to rise, the United States must explore innovative and sustainable solutions to ensure resource security and technological advancement. Recycling metals from the D-Block of the periodic table is a smart approach that not only addresses the increasing demand for critical minerals but also promotes environmental sustainability, resource conservation, and national security. By embracing recycling initiatives, the U.S. can lead the way in responsible resource management, fostering a resilient and secure future.



